Level 2
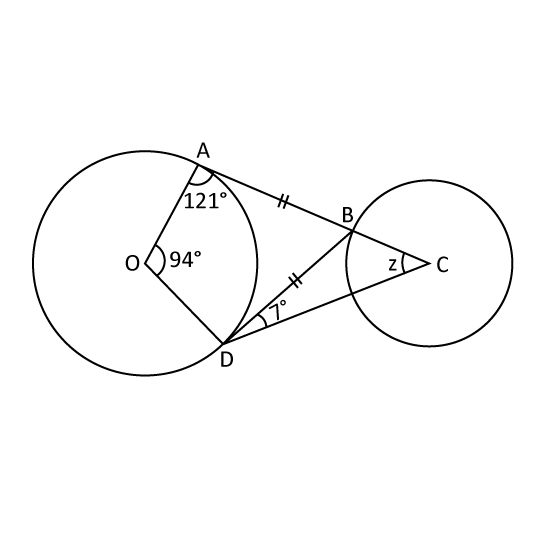
In the figure, not drawn to scale, O and C are the centres of the circles. AC is a straight line. Find ∠z.
Level 2
In the figure, not drawn to scale, O and C are the centres of the circles. AC is a straight line. Find ∠z.
Image in this question is not available.
Level 2
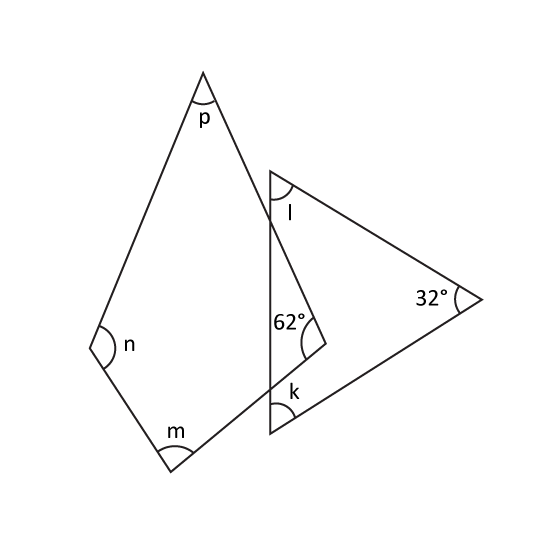
Find the sum of ∠m, ∠n, ∠p, ∠l and ∠k.
Level 2
Find the sum of ∠m, ∠n, ∠p, ∠l and ∠k.
Image in this question is not available.
Level 2
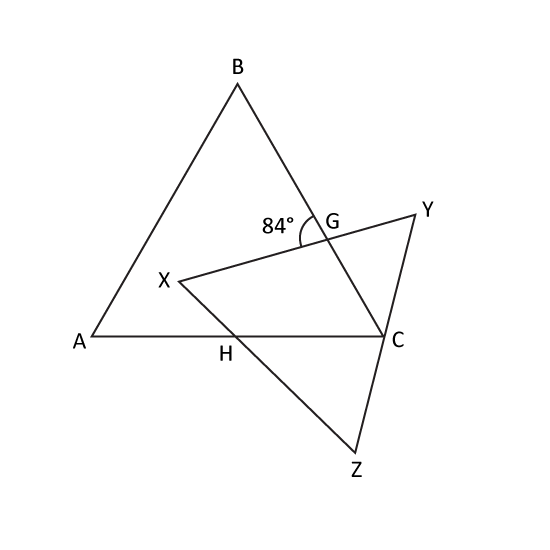
In the figure, ABC and XYZ are equilateral triangles and ∠BGX = 84°. Find ∠CHZ.
Level 2
In the figure, ABC and XYZ are equilateral triangles and ∠BGX = 84°. Find ∠CHZ.
Image in this question is not available.
Level 3
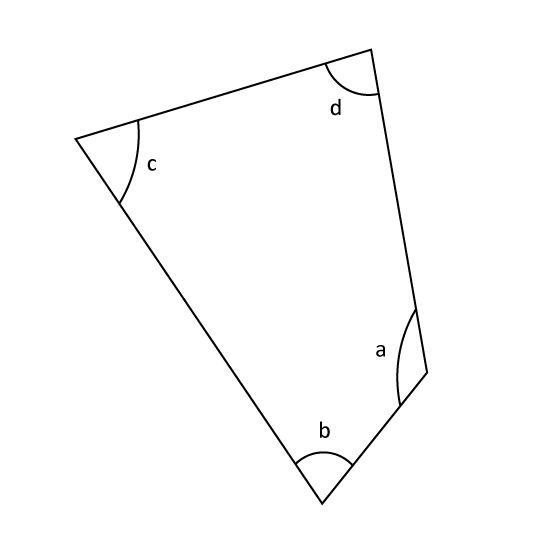
The figure is not drawn to scale. ∠c and ∠a are in the ratio 1 : 3. ∠b and ∠d are in the ratio 3 : 2. If ∠a = 105°, find ∠d.
Level 3
The figure is not drawn to scale. ∠c and ∠a are in the ratio 1 : 3. ∠b and ∠d are in the ratio 3 : 2. If ∠a = 105°, find ∠d.
Image in this question is not available.
Level 3
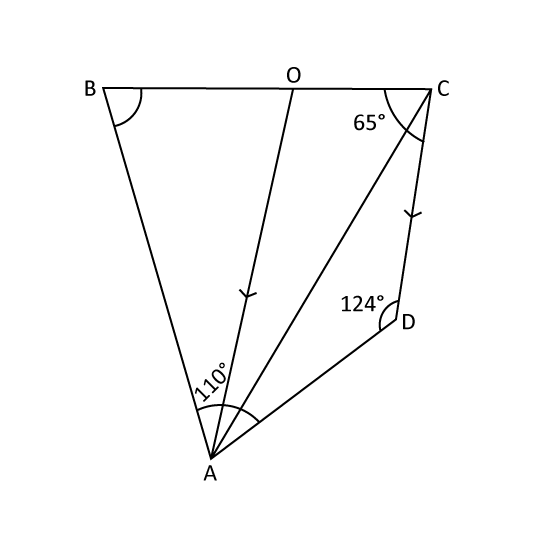
ABCD is a quadrilateral and OADC is a trapezium in which OA // DC and ∠BAD = 110°, ∠ADC = 124°, ∠BCD = 65° and DC = DA. Find
- ∠ABO
- ∠DAO
- ∠ACD.
Level 3
ABCD is a quadrilateral and OADC is a trapezium in which OA // DC and ∠BAD = 110°, ∠ADC = 124°, ∠BCD = 65° and DC = DA. Find
- ∠ABO
- ∠DAO
- ∠ACD.
Image in this question is not available.
Level 3
The figure, not drawn to scale, is made up of a triangle QRS, an equilateral triangle KLM and a trapezium NPRS. ∠SRP = 117°, ∠RPN = 63° and ∠PNS = 55°. Find the sum of ∠a, ∠b, and ∠c.
Level 3
The figure, not drawn to scale, is made up of a triangle QRS, an equilateral triangle KLM and a trapezium NPRS. ∠SRP = 117°, ∠RPN = 63° and ∠PNS = 55°. Find the sum of ∠a, ∠b, and ∠c.
Image in this question is not available.
Level 3
The figure, not drawn to scale, is made up of an equilateral triangle KLM and a trapezium ABCD. Find the sum of ∠x, ∠y and ∠z
Level 3
The figure, not drawn to scale, is made up of an equilateral triangle KLM and a trapezium ABCD. Find the sum of ∠x, ∠y and ∠z
Image in this question is not available.
Level 3
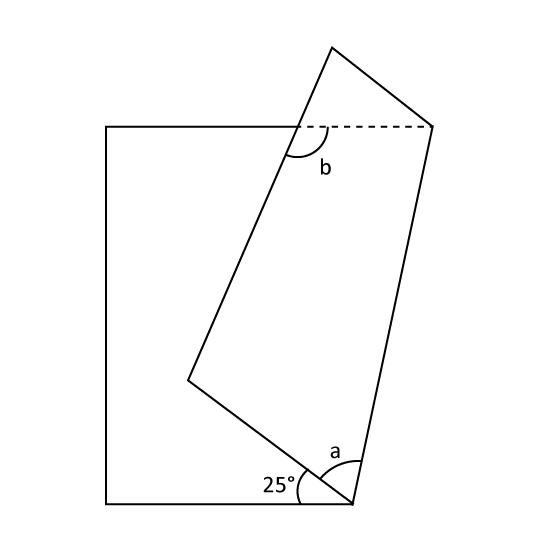
A rectangular piece of paper was folded as shown. Find ∠EGI.
Level 3
A rectangular piece of paper was folded as shown. Find ∠EGI.
Image in this question is not available.
Level 3
In the figure, not drawn to scale, JKL is an isosceles triangle, KLMN is a parallelogram and NKJ is a straight line. Find ∠NQP.
Level 3
In the figure, not drawn to scale, JKL is an isosceles triangle, KLMN is a parallelogram and NKJ is a straight line. Find ∠NQP.
Image in this question is not available.
Level 3
In the figure, not drawn to scale, ABC, CDE, BFE, and AFD are straight lines. What is the value of ∠x + ∠y?
Level 3
In the figure, not drawn to scale, ABC, CDE, BFE, and AFD are straight lines. What is the value of ∠x + ∠y?
Image in this question is not available.
Level 3
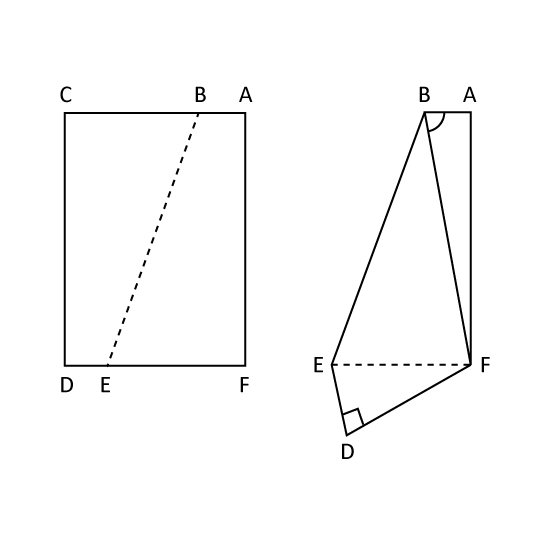
A rectangular piece of paper was folded as shown.
- Find ∠a.
- Find ∠b.
Level 3
A rectangular piece of paper was folded as shown.
- Find ∠a.
- Find ∠b.
Image in this question is not available.
Level 3
The figures are not drawn to scale. Figure 1 shows a rectangular piece of paper ACDF that measures 20 cm by 14 cm. AB = ED = 5 cm. The paper is folded along the dotted line BE such that point C touches point F, as shown in Figure 2.
- Find the area of Figure 2. ABEDF, after the folding.
- In Figure 2, ∠ABF is 76°. Find ∠BED in Figure 2.
Level 3
The figures are not drawn to scale. Figure 1 shows a rectangular piece of paper ACDF that measures 20 cm by 14 cm. AB = ED = 5 cm. The paper is folded along the dotted line BE such that point C touches point F, as shown in Figure 2.
- Find the area of Figure 2. ABEDF, after the folding.
- In Figure 2, ∠ABF is 76°. Find ∠BED in Figure 2.
Image in this question is not available.
Level 3
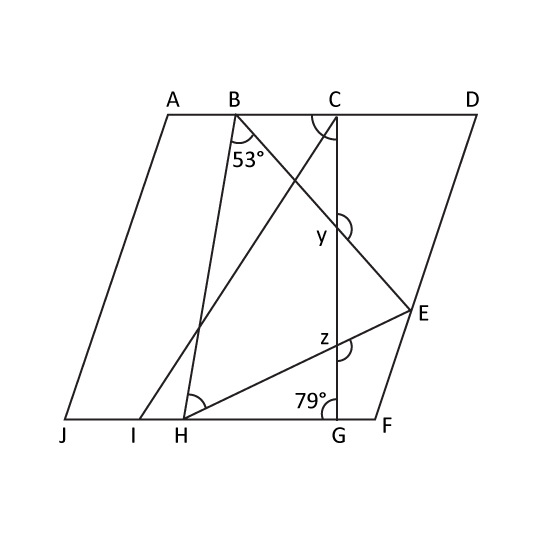
The figure is not drawn to scale. ADFJ is a parallelogram. CGI and BEH are triangles. ∠CGH = 79° and HBE = 53°. Find
- ∠BCG
- the sum of ∠BHE, ∠CYE and ∠EZG.
Level 3
The figure is not drawn to scale. ADFJ is a parallelogram. CGI and BEH are triangles. ∠CGH = 79° and HBE = 53°. Find
- ∠BCG
- the sum of ∠BHE, ∠CYE and ∠EZG.
Image in this question is not available.
Level 3
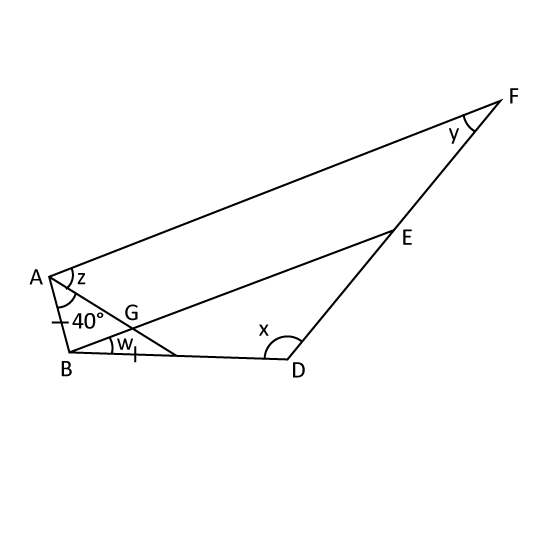
The figure is not drawn to scale. ∠BAC = 40°, BA = BC and AF//BE. Given that ∠z is
12 of ∠x and ∠z is 3 times of ∠y, find
- ∠z
- ∠w.
Level 3
The figure is not drawn to scale. ∠BAC = 40°, BA = BC and AF//BE. Given that ∠z is
12 of ∠x and ∠z is 3 times of ∠y, find
- ∠z
- ∠w.
Image in this question is not available.
Level 3
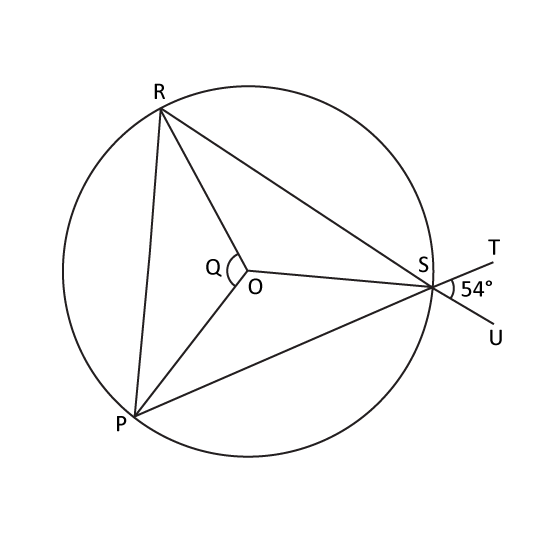
In the figure not drawn to scale, O is the centre of the circle and RSU and PST are straight lines. If ∠TSU = 54° and ∠RSO is twice of ∠OSP, find ∠Q.
Level 3
In the figure not drawn to scale, O is the centre of the circle and RSU and PST are straight lines. If ∠TSU = 54° and ∠RSO is twice of ∠OSP, find ∠Q.
Image in this question is not available.